QoS Control and Rx Interface Integration
The integration of Rx interface and QoS(Quality of Service) control is critical for ensuring mission-critical communication services (MCPTT, MCVideo, MCData) maintain the necessary performance, reliability and prioritization in LTE networks.
Overview
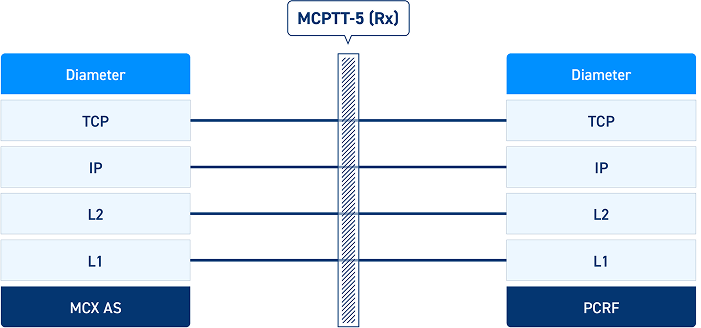
The Rx interface enables the MCX Application Server (MCX AS) to dynamically communicate with the PCRF (Policy and Charging Rules Function) within the LTE EPC (Evolved Packet Core) to control bearer setup, resource allocation and real-time QoS enforcement.
QoS mechanisms, particularly via QCI (QoS Class Identifier) settings, ensure that mission-critical services are prioritized even under network congestion.
Key Benefits
Dynamic QoS Enforcement: On-demand setup of dedicated EPS bearers based on service requirements.
Guaranteed Bitrate (GBR): Assures consistent media quality for PTT, video and data sessions.
Public Safety Prioritization: Ensures MCX traffic is prioritized over general internet or VoLTE traffic.
- Application-Controlled Resource Allocation: MCX AS directly manages bearer setup and updates via PCRF.
Integration Reference Points
- Rx interface MCX AS ↔ PCRF communication based on 3GPP TS 29.214
Gx Interface: PCRF ↔ PGW for bearer management enforcement
- Network Entities: MCX AS, PCRF, PGW, eNB
Diameter Signalling Over Rx
| Message | Purpose |
|---|---|
| AA-Request (AAR) | Request for dedicated bearer establishment |
| AA-Answer (AAA) | PCRF response to bearer request |
| Re-Auth-Request (RAR) | Bearer modification request |
| Session-Termination-Request (STR) | Release dedicated bearer |
- Encrypted Diameter messaging is supported.
- IPv4 and IPv6 sessions are both compatible.
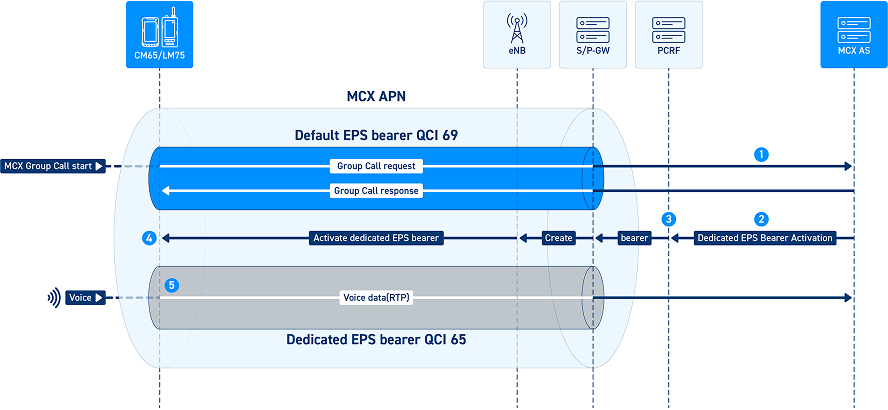
QoS Application Workflow
- Session Trigger : MCX AS detects initiation of a PTT, video or data session.
- AAR Message : Sent to PCRF which requesting specific QCI, bandwidth and priority.
- PCRF Authorization : PCRF checks policy and sends bearer setup instructions to PGW via Gx.
- Bearer Activation : PGW and eNB establish the EPS bearer with requested QoS parameters.
- Session Lifecycle Management : Updates (e.g., media bitrate changes) or termination (STR) handled dynamically.
QCI (QoS Class Identifier) in MCX
Each MCX service maps to specific QCI values to enforce differentiated treatment:
| QCI | Resource Type | Priority Level | Packet Delay Budget | Packet Error Loss Rate | Example Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GBR | 2 | 100 ms | 10⁻² | Conversational Voice |
| 2 | GBR | 4 | 150 ms | 10⁻³ | Conversational Video (Live Streaming) |
| 3 | GBR | 3 | 50 ms | 10⁻³ | Real-Time Gaming |
| 4 | GBR | 5 | 300 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Non-Conversational Video (Buffered Streaming) |
| 65 | GBR | 0.7 | 75 ms | 10⁻² | Mission Critical user plane Push-To-Talk voice (e.g., MCPTT) |
| 66 | GBR | 2 | 100 ms | 10⁻² | Non-Mission-Critical user plane Push-To-Talk voice |
| 5 | Non-GBR | 1 | 100 ms | 10⁻⁶ | IMS Signalling |
| 6 | Non-GBR | 6 | 300 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Video (Buffered Streaming), TCP-based services (e.g., www, email, chat, FTP, P2P file sharing) |
| 7 | Non-GBR | 7 | 100 ms | 10⁻³ | Voice, Video (Live Streaming), Interactive Gaming |
| 8 | Non-GBR | 8 | 300 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Video (Buffered Streaming), TCP-based services (e.g., www, email, chat, FTP, P2P file sharing) |
| 9 | Non-GBR | 9 | 300 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Same as QCI 8 |
| 69 | Non-GBR | 0.5 | 60 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Mission Critical delay-sensitive signalling (e.g., MC-PTT signalling) |
| 70 | Non-GBR | 5.5 | 200 ms | 10⁻⁶ | Mission Critical Data (same example services as QCI 6/8/9) |
Bearer Types
- Default Bearer (Non-GBR): Basic connectivity and signalling.
Dedicated Bearer (GBR or Non-GBR): For high-priority voice, video, and data traffic.
Logical Architecture
- MCX AS directly controls bearer lifecycle.
- PCRF enforces network policy based on real-time session needs.
- PGW and eNB coordinate for bearer establishment and QoS enforcement.
- Multiple bearer paths supported based on service class.
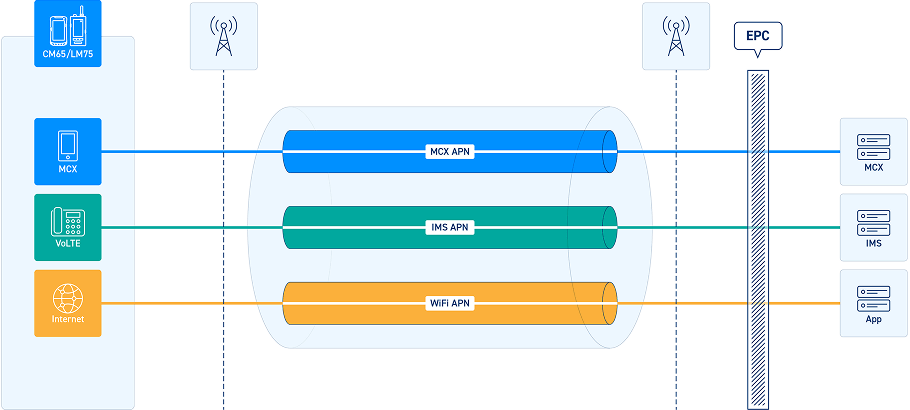
Cybertel’s QoS & Rx Integration Highlights
- Full 3GPP TS 23.203, TS 29.214 compliance.
- Proven interoperability with national LTE core networks.
- Seamless dedicated bearer management per MCX session.
- Dynamic QCI assignment and media rate control based on service demands.
- Support for public safety network deployment models, including separate MC-PTT APNs.
Why Choose Cybertel for Rx and QoS Integration?
- End-to-end dedicated bearer lifecycle management.
- Fully dynamic session-driven QoS enforcement.
- Real-time coordination between MCX services and LTE EPC.
- Proven reliability in large-scale, mission-critical deployments.